elisa test biology|antibody a level diagram : services The enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a powerful method for detecting and quantifying a specific protein in a complex mixture. Originally described by Engvall and Perlmann (1971), the method enables analysis of . The product information sheet for TX-100 that Sigma distributes claims it it stable to autoclaving, but honestly, I don't know why you would want to. I don't think I've ever felt the need to .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Discover the ultimate guide to steam (autoclave) sterilization for healthcare professionals. Learn the principles, processes, and critical role in patient care. In healthcare, ensuring the sterility of medical instruments is .
The enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a powerful method for detecting and quantifying a specific protein in a complex mixture. Originally described by Engvall and Perlmann (1971), the method enables analysis of .The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunological assay commonly used .Protein Biology Learning Center . When developing any new ELISA, it is important to test several different blockers for the highest signal to noise ratio in the assay. Many factors can influence nonspecific binding, including various .Explain the principle of the a direct ELISA test. detects presence of a specific antigen 1. Monoclonal antibodies bind to bottom of test plate. 2. Antigen molecules in sample bind to antibody. Rinse excess. 3. Mobile antibody with ‘reporter enzyme’ attached binds to antigens that are ‘fixed’ on the monoclonal antibodies. Rinse excess. 4.
What is an ELISA? The basic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), or enzyme immunoassay (EIA), is distinguished from other antibody-based assays because separation of specific and non-specific interactions occurs via serial binding to a solid surface, usually a polystyrene multiwell plate, and because quantitative results can be achieved.
Enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) use the catalytic properties of enzymes to detect and quantify immunologic reactions. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a heterogeneous EIA technique used in clinical analyses.[1] In this type of assay, one of the reaction components is nonspecifically adsorbed or covalently bound to the surface of a solid .Study with Quizlet and memorise flashcards containing terms like What does ELISA stand for?, What is the purpose of the ELISA test?, What can the ELISA test be used for? and others. . Biology - Chapter 24: Origins of species and macroevolution . 14 terms. ellesbelles09. Preview. BTEC Applied Science Unit 1 Biology. Teacher 118 terms . ELISA Data Interpretation. The ELISA assay yields three different types of data output: Quantitative: ELISA data can be interpreted in comparison to a standard curve (a serial dilution of a known, purified antigen) in order to precisely calculate the concentrations of antigen in various samples.
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), biochemical procedure in which a signal produced by an enzymatic reaction is used to detect and quantify the amount of a specific substance in a solution. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) typically are used to detect antigens, though they can also be used to detect other substances, including .
ELISA stands for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, also often referred to as enzyme immunoassay (EIA). An ELISA, like other types of immunoassays, relies on antibodies to detect a target antigen using highly specific antibody-antigen interactions. In an ELISA assay, the antigen must be immobilized to a solid surface.The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), is an antibody-based assay which has become one of the most commonly used methods to detect a variety of components from biological samples, including proteins, glycoproteins, antibodies, antigens, cytokines, etc., since its development over 50 years ago.ELISA test -A level Biology. 5.0 (2 reviews) Flashcards; Learn; Test; Match; Q-Chat; Get a hint. First stage of ELISA test. Antigen of interest is immobilised through a patients blood sample. 1 / 6. 1 / 6. Flashcards; Learn; Test; Match; Q-Chat; Isabella36050. Top creator on Quizlet. Share. Share. Students also viewed.A solution is added that contains a substrate that reacts with the enzyme attached to the secondary antibodies. If there are any secondary antibodies present, a coloured product is formed, causing the solution in the reaction vessel to change colour
ELISA tests are categorized into three categories based on the methods applied to bind antigen and antibodies, namely: Indirect and Direct ELISA. The crucial step is to immobilize the antigen of interest, which can be done directly on the test plate or indirectly via a .ELISA is a biochemical assay used in immunology to detect the presence of an antigen, antibody, or another protein. It takes its name from the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).. The basic principle behind ELISA is that if an antigen or antibody is present in a sample, it will bind to a specific antibody or antigen attached to a solid support. You can find all my A Level Biology videos fully indexed at https://www.freesciencelessons.co.uk/a-level-revision-videos/a-level-biology/In this video, we lo. ELISA assay - This immunological assay lecture explains about the elisa test procedure and principle behind the elisa assay including direct, indirect and sa.
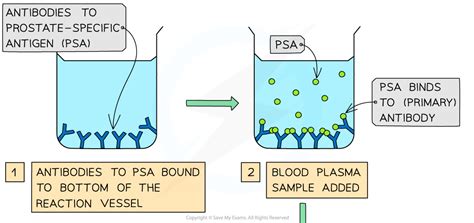
Ignore medical diagnosis/pregnancy/ PSA/ELISA test. 1 AQA Biology A-Level - The Immune System MS PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (c) Ignore mixing of direct or indirect ELISA Accept annotated diagram(s). . (indirect ELISA test). 4. (Substrate/solution added) and colour changes; Only award if enzyme mentioned. 4 [6] Q8. (a) 1. Bind to antigen OR
how is elisa test done
elisa test save my exams
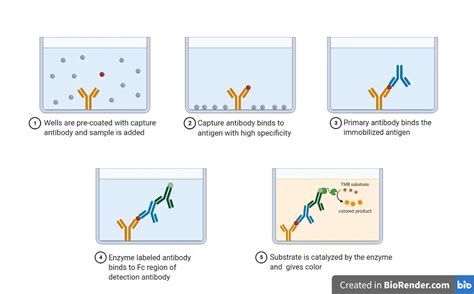
Quick explanation of how the elisa test works A level biology revision
Study with Quizlet and memorise flashcards containing terms like Describe the role of antibodies in producing a positive result in an ELISA test., Dengue fever is a human disease caused by the dengue virus. Scientists designed an ELISA test to detect antibodies to the dengue virus in a patient's blood sample. Suggest what is on the test at line T and explain what causes the line .
The test requires: the antibodies fixed to a solid surface, such as the inner surface of a test tube; a preparation of the same antibodies coupled to an enzyme — one (e.g., β-galactosidase) that produces a colored product from a colorless substrate. Performing the Test The tubes are filled with the antigen solution (e.g., urine) to be assayed.
Learn how monoclonal antibodies can be used in medical treatment, for example, to help treat cancer using bullet drugs. Learn how monoclonal antibodies can .
What is Sandwich ELISA? The sandwich ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) is a widely used technique in immunology and biochemistry to quantify the concentration of specific antigens in a sample. It derives its name from the fact that the antigen of interest is sandwiched between two layers of antibodies, known as the capture antibody and the . This second antibody-enzyme complex constitutes the indicator system of the test. The antigen serves as bridge, so the more antigen in the test solution, the more enzyme-linked antibody will bind. The test solution is used in parallel with a series of standard solutions with known concentrations of antigen that serve as control and reference. This video explains how antibodies are used to test for HIV. ELISA stands for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay - the final result is determined by a colour .Ø The sandwich or indirect ELISA addresses this issue by using a “capture” antibody specific to the test antigen, isolating it from the serum’s molecular mixture. Sandwich ELISA: Sandwich ELISA uses two antibodies—the first one captures the antigen and the second one, which is enzyme-linked, detects it.
The enzyme used in ELISA is horseradish peroxidase. Acetylcholinesterase and catalase are also the enzymes used in the ELISA test. Materials for ELISA. Performing an enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay ELISA involves a minimum of one antibody with specificity for a specific antigen. ELISA- Principle, Types and Applications. ELISA is an antigen antibody reaction. In 1971, ELISA was introduced by Peter Perlmann and Eva Engvall at Stockholm University in Sweden. It is a common laboratory technique which is usually used to measure the concentration of antibodies or antigens in blood.
Throughout this book excellent use is made of flow diagrams, graphs and tables to aid the reader. . The ELISA Guidebook is a must for institutional libraries, departments of immunology, hospital diagnostic laboratories, research laboratories using ELISA-based assays and companies developing ELISA immunodiagnostic kits.
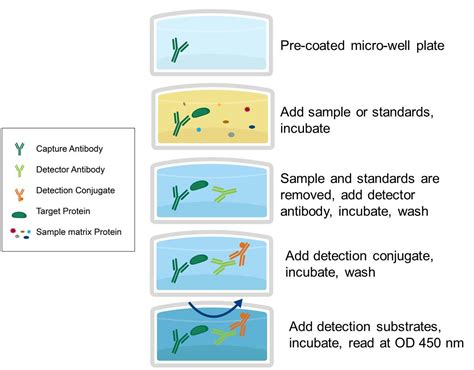
elisa test explained
elisa test diagram
For small batches of agar plates or low-volume media, you can use a pressure cooker, those wonderful commercial devices that cost ~$100. Here’s one tutorial and a quick search yields plenty of others as well as .
elisa test biology|antibody a level diagram